If you pull up any tire from the edge of the docks at Friday Harbor Laboratories, you’ll find a multitude of organisms — algae, bryozoans, hydroids, tube worms, and tunicates growing on the surface, and many more mobile organisms such as crabs, shrimp, urchins, copepods, and a variety of worms living in the habitat thus created.

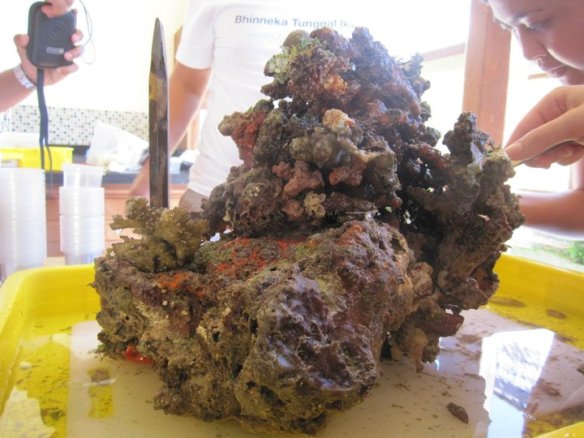
Figure 1 — Mussel (left), limpet (upper right), and rock (lower right), overgrown with a variety of organisms
On the benthos, a similar situation exists — any available substrate, living or not, is swiftly colonized by a variety of organisms. The rock in figure 1, though relatively small, is home to Terebratalia transversa, a brachiopod; red algae; at least four species of encrusting bryozoans; small calcareous tubes which could belong to gastropods or serpulid polychaetes; and two larger worm tubes, one containing its worm (Sabellaria), one containing a hermit crab (Discorsopagurus). Living substrates are likewise colonized; the mussel in figure 1, which was dredged from the same location as the rock, is overgrown by Balanus, the acorn barnacle; T. transversa; and at least two types of thecate hydroids. Finally, the limpet (next to the mussel in figure 1) carries on its back the calcareous bryozoan Heteropora, spionid polychaetes, Balanus, red algae, and an encrusting bryozoan. This sort of overgrowth of some organisms by others is an inevitable consequence of the scarcity of space in the marine benthos. Some, such as cheilostome bryozoans with their grabbing avicularia, combat the encrustation. Some, like the mussels and the limpet, ignore it. Finally, some organisms take advantage of it.
The decorator crab (Oregonia gracilis) is named for the patchwork of organisms which it purposefully attaches onto hooked setae on its carapace. Once emplaced, the organisms establish and grow there. This camouflaging cloak of colonists serves to confuse predators, and the makeup of the decorations is known to vary from one place to another, since these crabs choose their decorations from locally-available materials (Wickstein 1992). Decorator crabs are commonly seen on the support posts of the dock here at Friday Harbor, below the water line, so I went down to the dock with a net and a bucket to catch a few and see what they had attached to their carapaces.
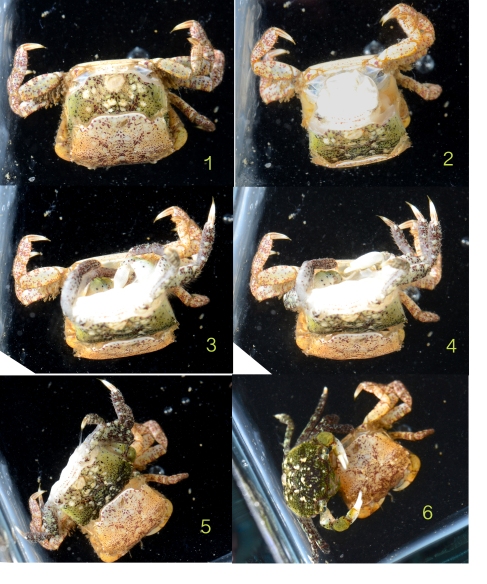
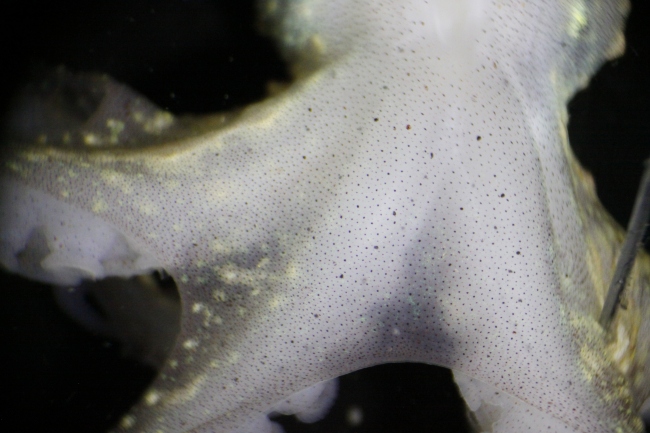
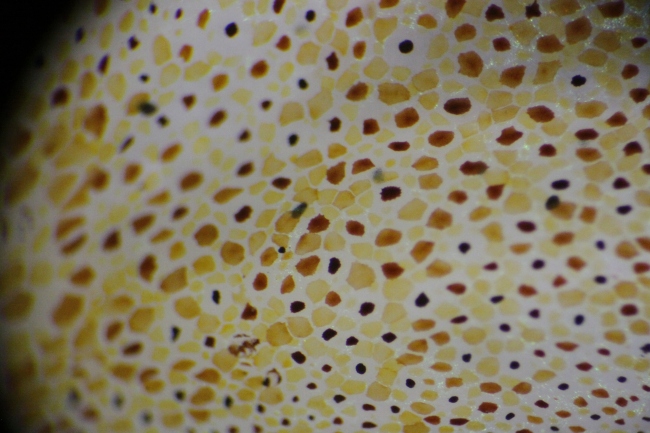
I caught three O. gracilis individuals. My first impression of their decorations was that in contrast to the rock, mussel, and limpet I examined earlier, the crabs’ encrusting biota was much more uniform. While the rock had patches of bryozoans and clumps of worm tubes, and the mussel’s hydroids were concentrated at one end, the crabs had organisms evenly distributed over their carapaces. Furthermore, the community composition of different parts of a crab’s carapace was similar; crabs with bryozoans on their backs also had the same type of bryozoans on their legs (Figs. 2, 4), and a crab with spots of sponge on its back had spots of the same sponge on its legs (Fig. 3). In contrast, the rock and mussel communities were much patchier.
So, what lives on the carapaces of decorator crabs at Friday Harbor? Let’s take a look.

Figure 2 — Dorsal view of O. gracilis with Dendrobenia lichenoides, red algae, yellow sponge, Corella willmeriana (transparent tunicate), four hydroids, and diatoms
The first crab I caught (Fig. 2) had attached a large frill of the bryozoan Dendrobaenia lichenoides to its rostrum. Smaller flakes of D. lichenoides were attached to its carapace and legs. Among the bryozoans grew at least four species of colonial hydroids. Diatom chains were stuck among the hydroids in many places; since those were not attached directly to the carapace, I am not sure whether or not the crab did that on purpose. Finally, the crab had finished off its decorations with a few bits of red algae, some unidentified yellow sponge, and a transparent tunicate which it carried along on one leg.

Figure 3 — Dorsal view of O. gracilis with Dendrobenia lichenoides, green algae, red algae, and unidentified hydroids
The second crab (Fig. 3), smaller than the first, was thickly adorned with D. lichenoides and a number of hydroids. It added some heterogeneity into its camouflage with some flecks of red and green algae.

Figure 4 — Dorsal view of O. gracilis with Dendrobenia lichenoides, yellow sponge, red algae, and green algae
The third crab (Fig. 4), like the first two, had also placed D. lichenoides all over its body. Unlike the first two, however, it had also polka-dotted itself with yellow sponges. It also had a few flecks of red and green algae, but no hydroids that I could find.
While the species composition from one crab’s carapace to another is not identical, a number of similarities emerge. Overall, the crabs appear to have attached leafy or dendritic, neutral-colored, colonial animals over most of their carapaces, and then added smaller patches of brighter-colored materials. The species on their carapaces are all common on local non-living substrates; for instance, it is easy to find Dendrobaenia on the dock tires. Finally, just like the bryozoans, algae, and hydroids on the dock tires and the dredged rocks and mussel, the habitat built by the decorator crabs on their carapaces provides a home for a number of other species; I found a number of amphipods, nematodes, and polychaetes living amongst their bryozoans and hydroids. Thus, while decorator crabs purposefully cultivate sessile organisms for their camouflage, they incidentally attract more mobile organisms as well and thus carry full-fledged communities on their backs.
Nadia Pierrehumbert
University of Chicago
REFERENCES
Wicksten, Mary K. 1993. A review and a model of decorating behavior in spider crabs (Decapoda, Brachyura, Majidae). Crustaceana 64(3).